Tips for optimizing automatic meter reading accuracy for water utilities
Capturing accurate meter data is essential to maintain system efficiency and productivity. When establishing automatic meter reading (AMR), advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and advanced metering analytics (AMA) systems, there are several steps to consider to get maximum performance from your new system.
To improve customer service and operational efficiencies, reduce non-revenue water loss and more accurately measure and conserve resources, an increasing number of utilities are deploying automated and smart metering initiatives.
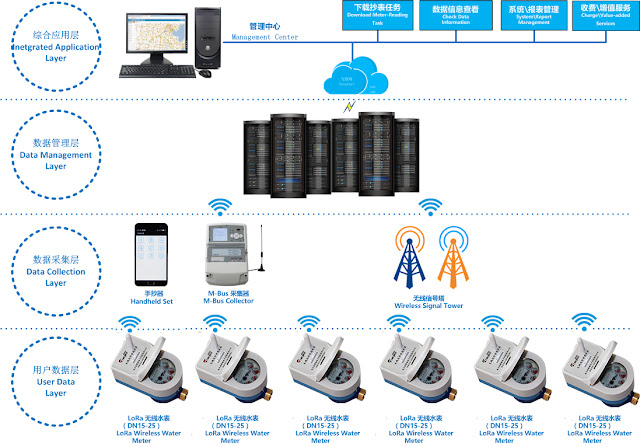
Known as automatic meter reading (AMR), advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and advanced metering analytics (AMA), these systems provide more frequent, efficient, and accurate meter reading data that can be relayed to a utility's database and billing systems. Gathering accurate meter data is vital to maintain system efficiency and productivity.
Understanding RF Technology
The radio signal through which most AMR/AMI/AMA systems communicate is an electromagnetic wave that vibrates—or oscillates—from the transmitting antenna. The wave's movement as it leaves the transmitting antenna into the air is called radio frequency propagation. The strength of this signal is affected by various factors, including:
-Distance between the endpoint and receiver.
Installation
Ideally, the pathway between the transmitter and receiver should be unobstructed. However, buildings, trees, and uneven terrain often get in the way. Therefore, utilities may want to test signal-reception strength at several potential reading locations to ensure the best location is chosen. Because a radio signal is broadcast in a 360-degree pattern, it must be able to propagate outward with little or no interference. Endpoint and receiver antennas must be vertically positioned to allow for the strongest data reads.
Data collectors should be mounted to provide a clear line of site between the transmitter and receiver.
Here are some additional guidelines for successful installations:
-Carefully follow manufacturers' guidelines, especially for monitoring endpoint orientation.
-Look for a clear line-of-site between the transmitter and receiver.
-Ensure registers and meters are correctly paired by size, model and registration type. Failure to do so can lead to inaccurate readings.
-Locate the endpoint to minimize obstructions, such as large, dense, or metal objects.
-Consider a remote transmitter mounted in basement joists or on the outside of a building.
-Mount remote transmitters as high as possible.
-Pit applications must have the endpoint mounted through the lid or properly positioned just below the lid. An endpoint simply dropped into a pit most likely will perform poorly.
Meter Reading and Data Management
Work order and equipment installation processes are key factors in ensuring the most accurate reads. A manual work order process leaves room for human error and subjects the utility to the possibility of recording incorrect information. A more efficient approach is a paperless work order system.
Keep in mind the following meter reading tips:
-Maintain a clear line-of-sight between the endpoint and receiver.
-If the endpoint is difficult to read, try different angles of approach.
-Walking/driving at a slower-than-normal speed might improve the results of hard-to-read endpoints.
-Implement electronic interface file transfers and electronic work order systems to eliminate most, if not all, manual data entry.
Walking at a slower-than-normal speed might improve the results of hard-to-read endpoints.
Maintenance and Testing
To ensure your meters remain accurate, it is vital to keep up with general maintenance and testing practices.
To improve customer service and operational efficiencies, reduce non-revenue water loss and more accurately measure and conserve resources, an increasing number of utilities are deploying automated and smart metering initiatives.
Known as automatic meter reading (AMR), advanced metering infrastructure (AMI) and advanced metering analytics (AMA), these systems provide more frequent, efficient, and accurate meter reading data that can be relayed to a utility's database and billing systems. Gathering accurate meter data is vital to maintain system efficiency and productivity.
The radio signal through which most AMR/AMI/AMA systems communicate is an electromagnetic wave that vibrates—or oscillates—from the transmitting antenna. The wave's movement as it leaves the transmitting antenna into the air is called radio frequency propagation. The strength of this signal is affected by various factors, including:
-Distance between the endpoint and receiver.
-Absorption of energy into obstructions such as buildings, trees, concrete walls, and other dense objects.
-Reflection of the signal off of metal structures such as siding, chain link fences, vehicles, and water towers.
To maintain the strongest signal and help ensure accurate data collection, keep the following tips in mind during installation, meter reading and maintenance of smart metering systems.
To maintain the strongest signal and help ensure accurate data collection, keep the following tips in mind during installation, meter reading and maintenance of smart metering systems.
Ideally, the pathway between the transmitter and receiver should be unobstructed. However, buildings, trees, and uneven terrain often get in the way. Therefore, utilities may want to test signal-reception strength at several potential reading locations to ensure the best location is chosen. Because a radio signal is broadcast in a 360-degree pattern, it must be able to propagate outward with little or no interference. Endpoint and receiver antennas must be vertically positioned to allow for the strongest data reads.
Data collectors should be mounted to provide a clear line of site between the transmitter and receiver.
Here are some additional guidelines for successful installations:
-Carefully follow manufacturers' guidelines, especially for monitoring endpoint orientation.
-Look for a clear line-of-site between the transmitter and receiver.
-Ensure registers and meters are correctly paired by size, model and registration type. Failure to do so can lead to inaccurate readings.
-Locate the endpoint to minimize obstructions, such as large, dense, or metal objects.
-Consider a remote transmitter mounted in basement joists or on the outside of a building.
-Mount remote transmitters as high as possible.
-Pit applications must have the endpoint mounted through the lid or properly positioned just below the lid. An endpoint simply dropped into a pit most likely will perform poorly.
Work order and equipment installation processes are key factors in ensuring the most accurate reads. A manual work order process leaves room for human error and subjects the utility to the possibility of recording incorrect information. A more efficient approach is a paperless work order system.
Keep in mind the following meter reading tips:
-Maintain a clear line-of-sight between the endpoint and receiver.
-If the endpoint is difficult to read, try different angles of approach.
-Walking/driving at a slower-than-normal speed might improve the results of hard-to-read endpoints.
-Implement electronic interface file transfers and electronic work order systems to eliminate most, if not all, manual data entry.
Maintenance and Testing
To ensure your meters remain accurate, it is vital to keep up with general maintenance and testing practices.
-Create a comprehensive maintenance and testing plan. Unique variables in some locations may necessitate meter repair or replacement more often than in other locations.
-Seasonal changes, increasing vegetation and building construction may cause a signal to change over time.
-Keep pit lids free of dirt, grass and other debris.
Be aware that an AMR/AMI endpoint radio frequency signal may be affected by various sources, such as the factors listed above. Use the tips in this article to help your utility gather the most accurate meter data.
Be aware that an AMR/AMI endpoint radio frequency signal may be affected by various sources, such as the factors listed above. Use the tips in this article to help your utility gather the most accurate meter data.



评论
发表评论